The San Andreas Fault: Facts about the crack in California’s crust that could unleash the ‘Big One’

Quick facts about the San Andreas Fault
How long is the San Andreas Fault? About 746 miles (1,200 kilometers)
What was the biggest earthquake on the San Andreas Fault? The Great San Francisco Earthquake of 1906, which had a magnitude of around 7.9
When was the San Andreas Fault discovered? 1895
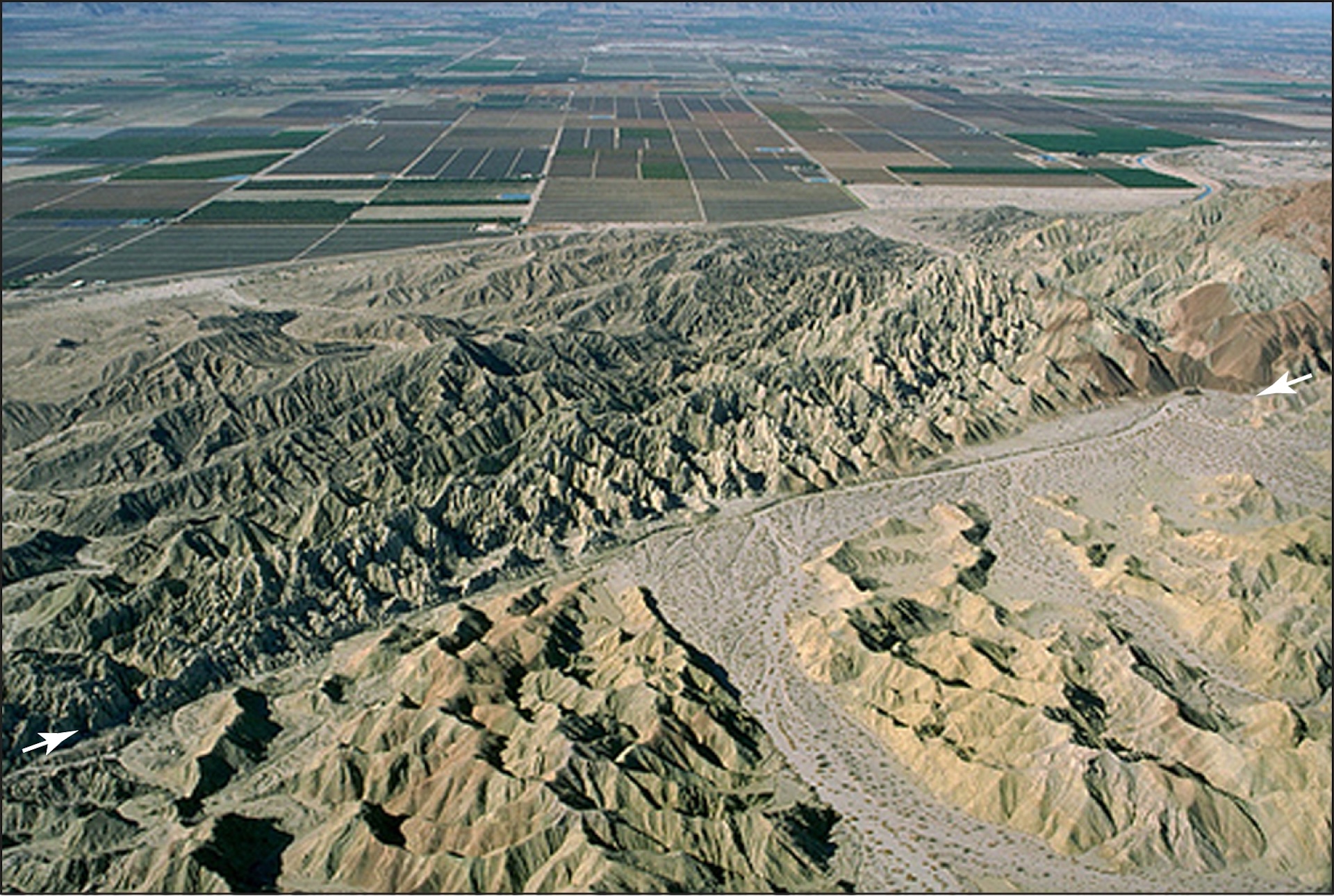
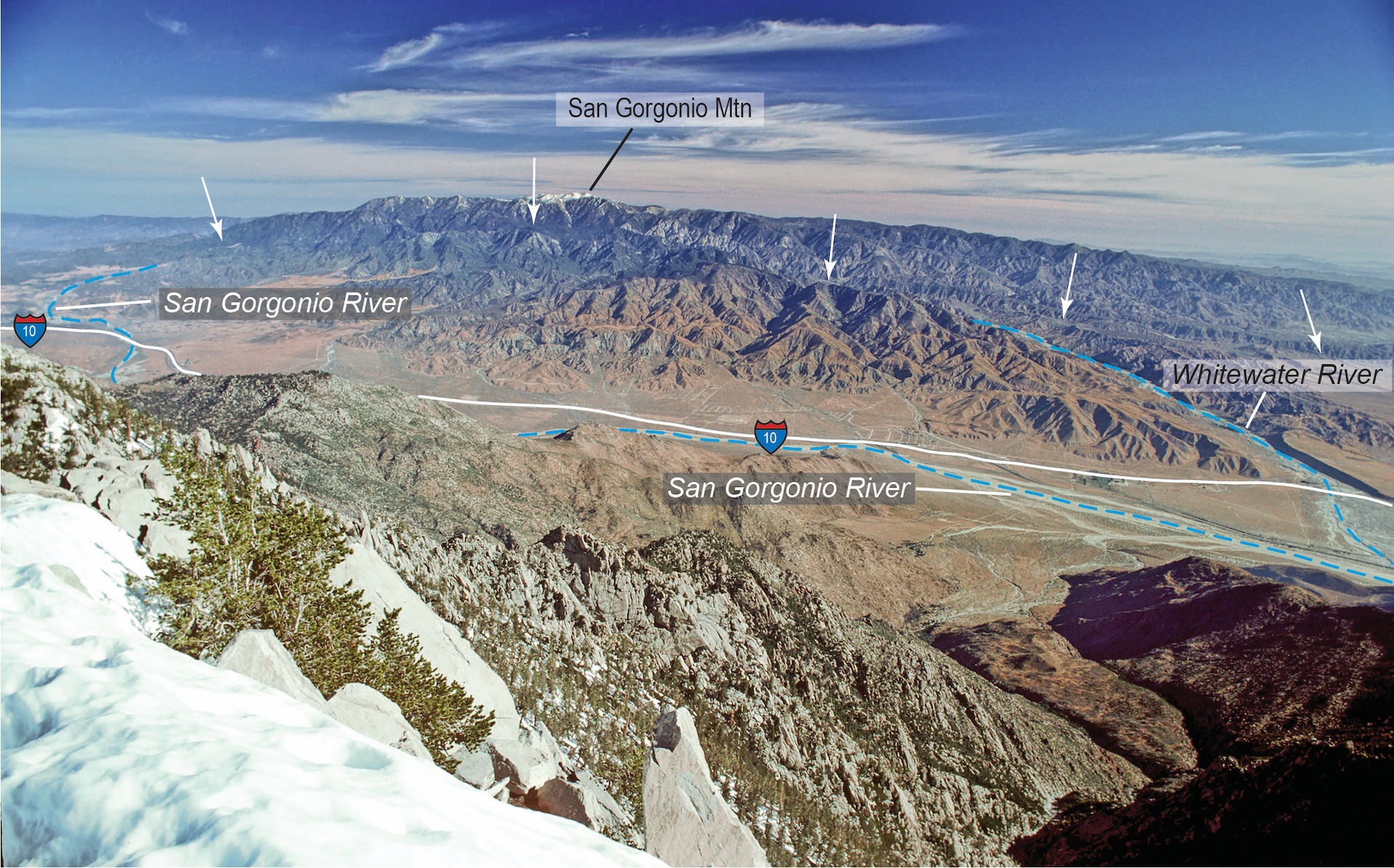
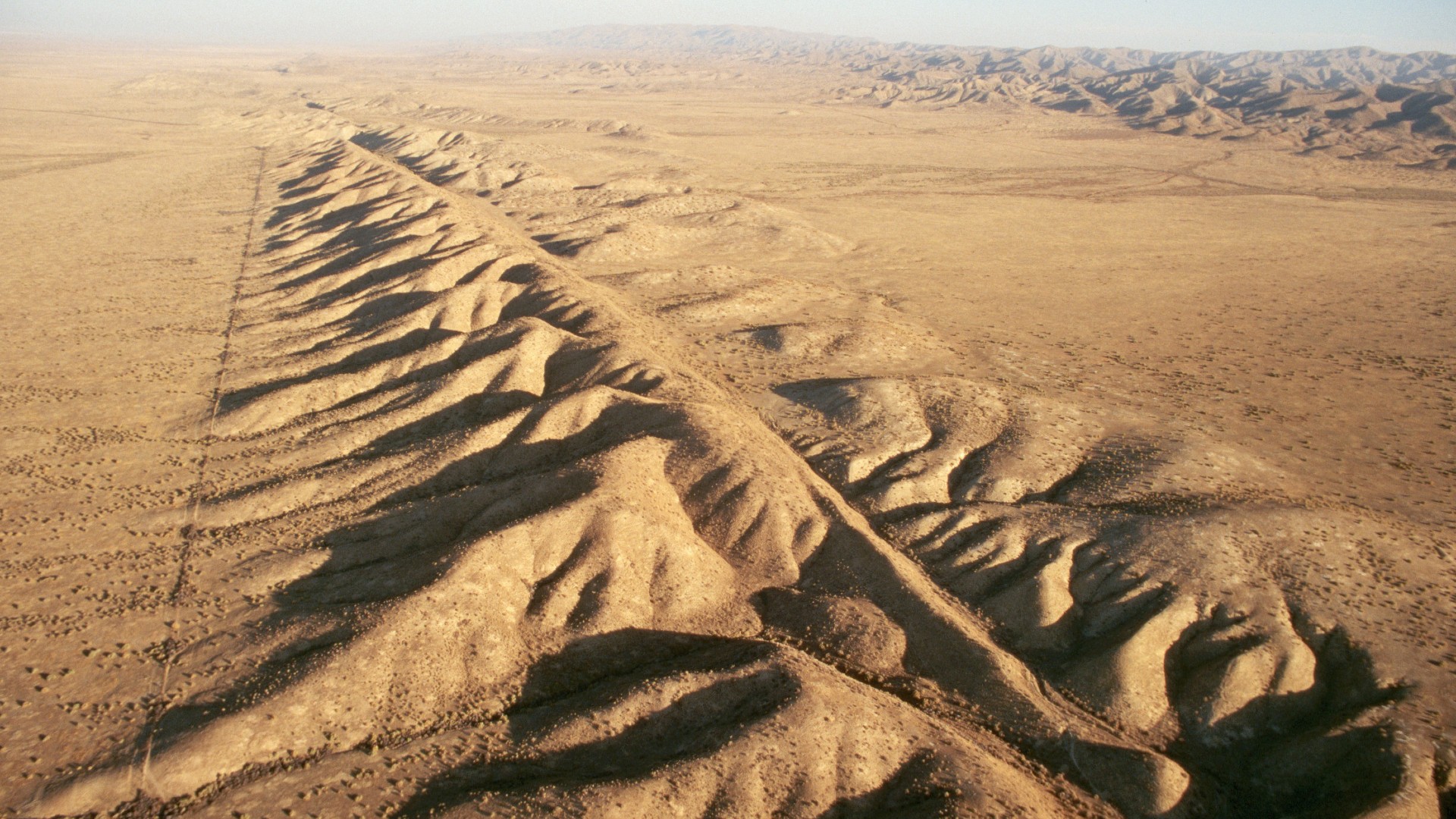
The San Andreas Fault is California’s longest and most famous fault. At this fracture zone, two plates of Earth’s crust move past each other. It stretches from the Salton Sea in Southern California to off the coast of Mendocino in Northern California. On the inland side of the fault, the North American Plate moves southeast. Toward the coast, the Pacific Plate creeps northwest.
The San Andreas is capable of creating big, destructive earthquakes. Earthquakes are measured in magnitude on a scale that starts at zero. In this scale, each whole number represents an earthquake 10 times as large as the one before it. Most earthquakes under magnitude 2.5 aren’t felt, while 2.5- to 5.4- magnitude quakes usually cause some shaking but not much damage. Quakes of 5.5 magnitude and higher cause damage to buildings, and earthquakes over 7.0 are considered major.
In 1906, the northern section of the fault shook San Francisco and the Bay Area with a 7.9 magnitude quake, which caused a devastating fire in the city and killed more than 3,000 people, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. In 1857, the southern section of the fault shook and created a quake thought to be just as large. Only two people died, because California had a tiny population at the time. Geologists warn that the San Andreas will give off a large earthquake again — the only question is when.
5 fast facts about the San Andreas Fault
- Over the past 3 million years, the San Andreas Fault has moved an average of 2 inches (56 mm) per year.
- If that rate continues, Los Angeles and San Francisco will be next-door neighbors in 15 million years!
- The 1857 Fort Tejon quake on the southern San Andreas Fault lasted between one and three minutes.
- During the 1906 Great San Francisco earthquake, 296 miles (477 km) of the fault moved.
- The San Andreas Fault was discovered just 11 years before the 1906 earthquake by geologist Andrew Lawson, who worked at the University of California, Berkeley.
Everything you need to know about the San Andreas Fault
What type of fault is the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is a “right-lateral strike-slip fault.” That’s a complicated way to say that if you stood on the North American Plate side of the fault facing the Pacific Ocean, the Pacific Plate side of the fault would be moving slowly to the right. At the San Andreas, the two plates are like blocks that are moving past each other and sometimes getting stuck along the way. When they get unstuck — quickly! — the result is a sudden earthquake.
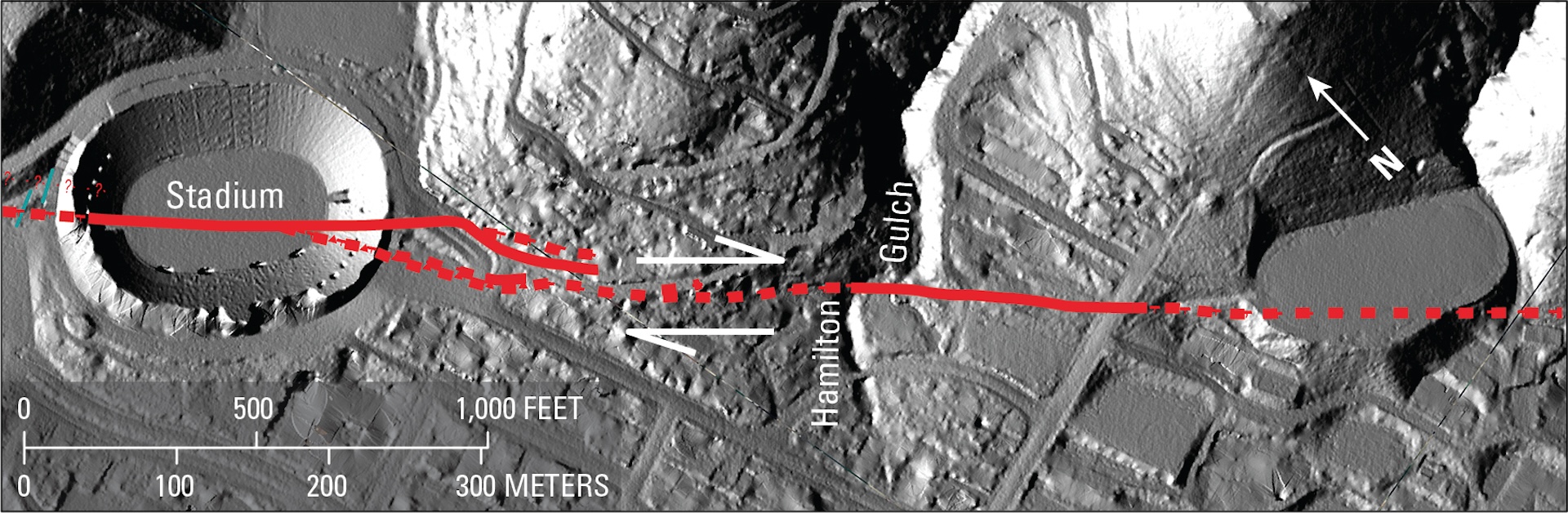
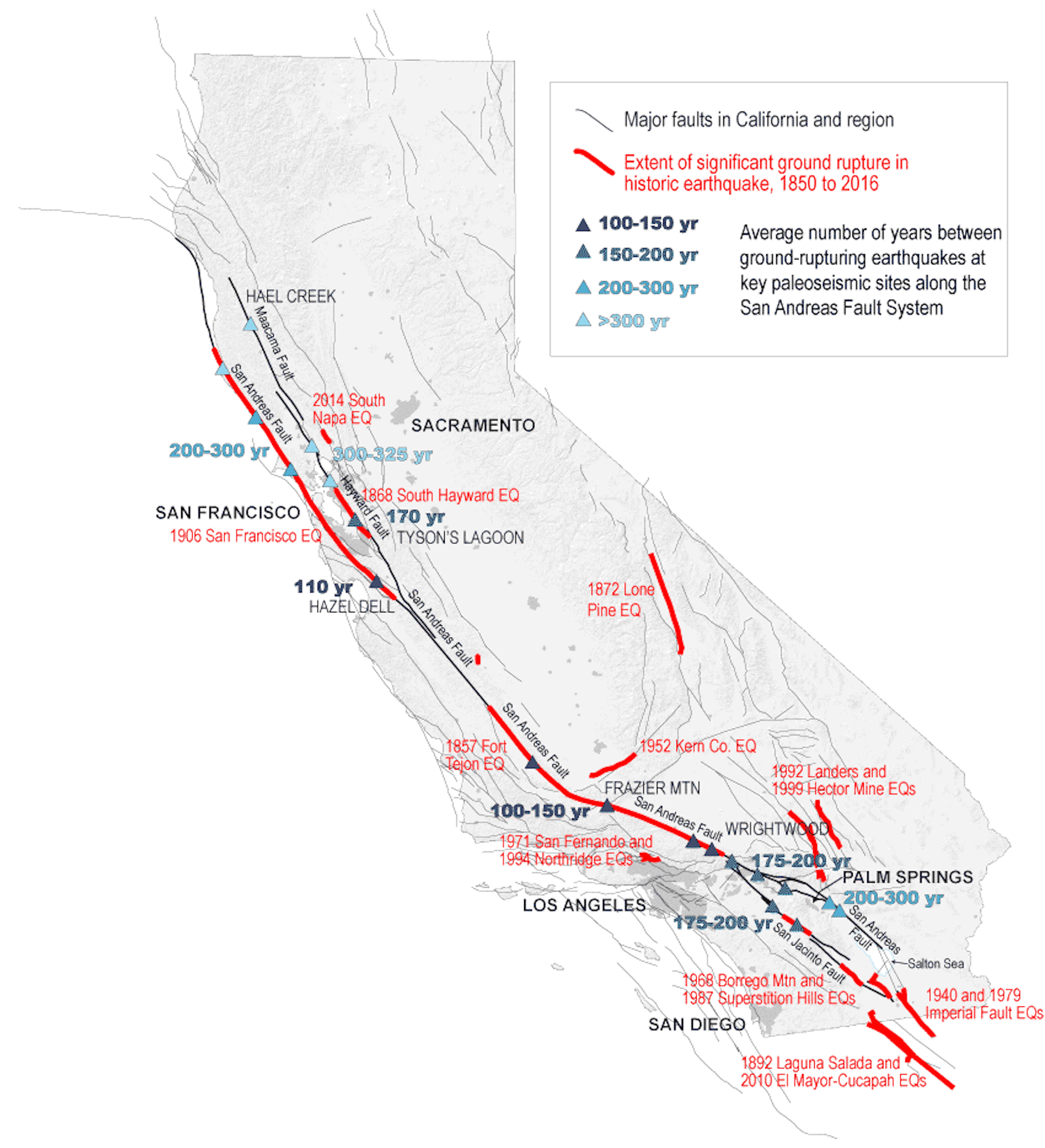
The fault is split into three segments. The southern segment starts northeast of San Diego at Bombay Beach, California, and continues north to Parkfield, California, near the middle of the state. A quake on this segment would threaten the highly populated city of Los Angeles.
The middle section of the San Andreas is known as the “creeping section.” It stretches between the California cities of Parkfield and Hollister in central California. Here, the fault “creeps,” or moves slowly without causing shaking. There haven’t been any large quakes on this section within recorded history, but scientists think there may have been earthquakes there at some point in the past 3 million years.
Finally, the northern section of the San Andreas spans from Hollister to a special spot called the “triple junction” off the coast of Mendocino. The triple junction is where the North American tectonic plate, Pacific plate, and undersea Gorda plate meet. At this junction, the way the plates move past each other on the San Andreas Fault transforms into a different kind of geology known as a subduction zone. In the subduction zone, the Pacific Plate slides under the North American Plate instead of alongside it.
How long and deep is the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is about 746 miles (1,200 km) long and about 10 miles (16 km) deep. While the San Andreas is a giant fault that is even visible from space, if you zoom in, you’ll see a network of many faults coming off the San Andreas.
So the whole region is known more generally as the San Andreas Fault zone. This area includes faults like the Hayward Fault, which runs through the East Bay area. These side faults can produce their own serious earthquakes. For example, in 1868, the Hayward Fault rumbled to life with a magnitude 6.8 quake that killed 30 people. A similar quake today would affect the Bay Area, where millions of people live.
How did the San Andreas Fault form?
A long time ago, the tectonic plate under the Pacific Ocean crashed directly into the tectonic plate carrying the continent of North America. The ocean plate dove under the continental plate, a pattern called subduction. Meanwhile, in the middle of the ocean there was a spot where molten lava, or magma, rose from inside Earth and formed brand-new crust.
The place where the new crust formed wasn’t very far from the subduction zone where crust got pushed back into the Earth. So about 30 million years ago, those two spots came together. The place where the new crust formed got pushed right under North America!
This was a big change in how the geology worked in all of western North America. A new ocean plate was now touching North America. It was moving in a slightly different direction, so it didn’t dive right under the continent. Subduction ended, and a new strike-slip fault (the San Andreas) was formed.
How dangerous is the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault runs through and near many populated areas, including Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area. It can produce damaging earthquakes, so scientists consider it a very dangerous fault.
Geologists estimate that the southern San Andreas could produce a quake of up to magnitude 8.3. As far as they know, the fault hasn’t ever produced a quake larger than the 1857 or 1906 quakes, both of which were probably around magnitude 7.9.
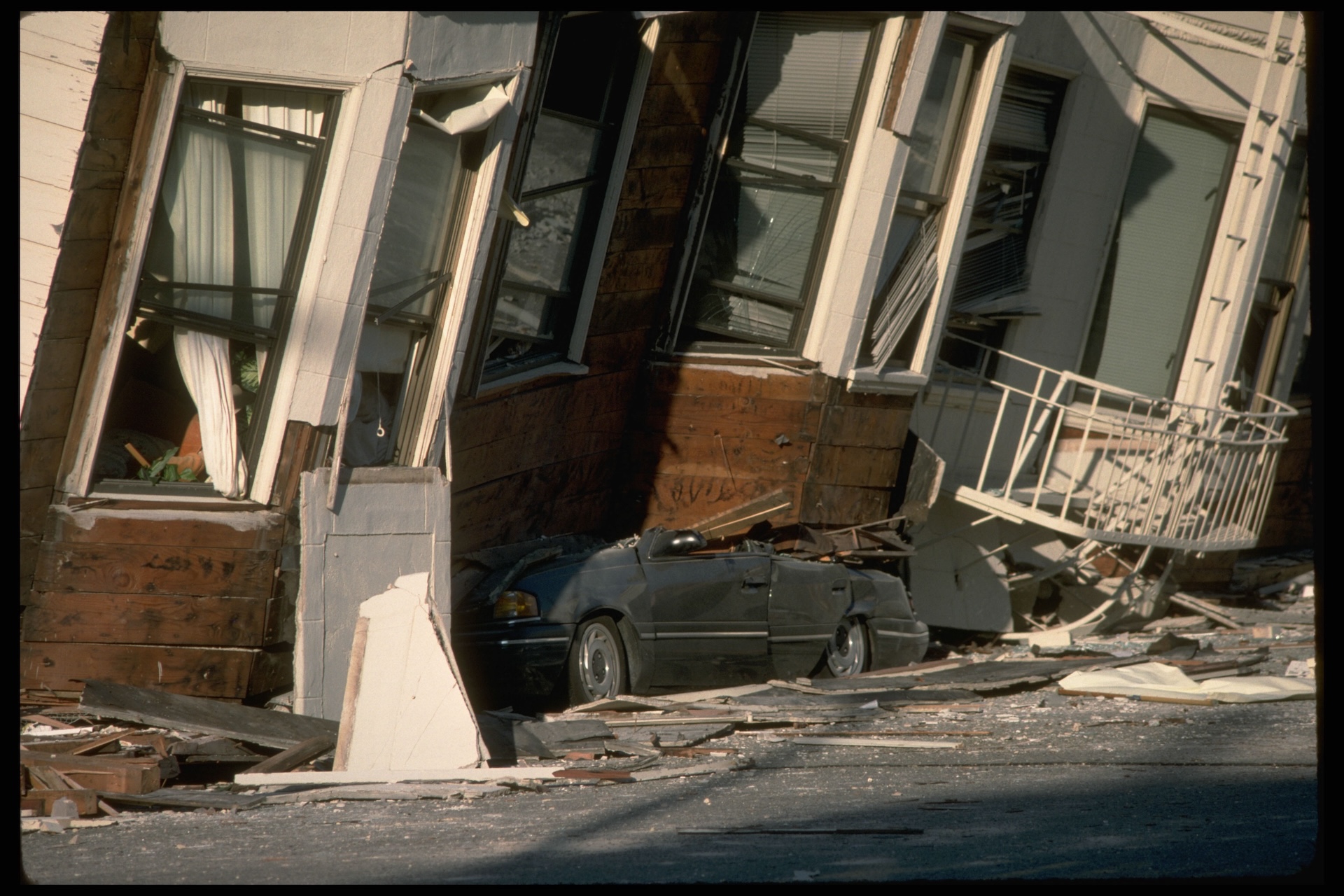
That is plenty destructive, though. The magnitude 6.9 Loma Prieta earthquake that hit the Bay Area in 1989 killed 63 people. And remember that earthquake magnitude goes up by 10 for every whole number, so a magnitude 8.3 would be more than 25 times bigger than the Loma Prieta quake.
If a magnitude 7.8 quake were to hit the southern San Andreas, geologists expect it would cause 1,800 deaths, 50,000 injuries and $200 billion in damage.

Can scientists predict the next big earthquake on the San Andreas Fault?
Scientists can’t predict when the next San Andreas earthquake — or any earthquake — will occur. But they can get an idea of the future risk by looking at how often earthquakes have occurred in the past. On the southern San Andreas, some sections seem to give off a good shake every 100 years or so, while others go as long as 300 years between major quakes. The Fort Tejon area, about 70 miles (113 km) north of Los Angeles, typically sees a large quake every 100 to 150 years. The last time it had a large earthquake was in 1857, so that area is considered overdue.
The average time between earthquakes depends on the fault or section of the fault.They’re not always the same; they can vary by years or decades. Also, dangerous quakes can happen on side faults that scientists don’t even know about. The magnitude 6.7 Northridge earthquake that struck Los Angeles in 1994 happened on a fault geologists previously didn’t know existed. This fault wasn’t part of the San Andreas, but it was a nearby fault affected by the San Andreas’ motion.
The U.S. Geological Survey, which tracks faults and measures earthquakes, has calculated that there’s a 72% chance of a magnitude 6.7 earthquake in the San Francisco Bay region by 2043. And there’s a 60% chance of a quake of 6.7 or larger in that time frame in the Los Angeles region.
San Andreas Fault pictures
Discover more about earthquakes
Source link