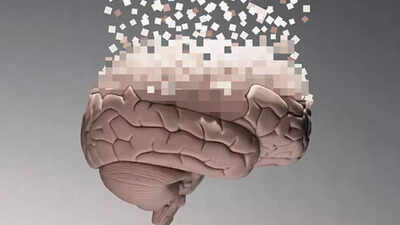
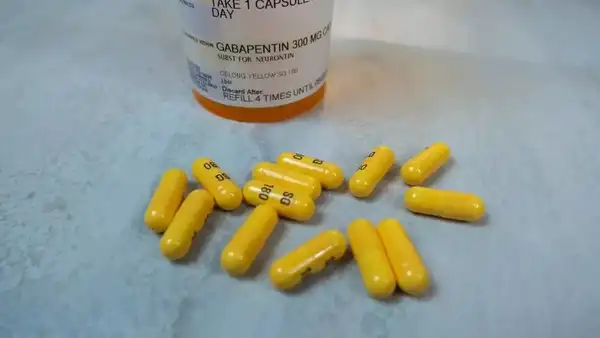
Gabapentin side effects: Popularly prescribed pain drug can increase the risk of dementia by up to 40%, reveals study |
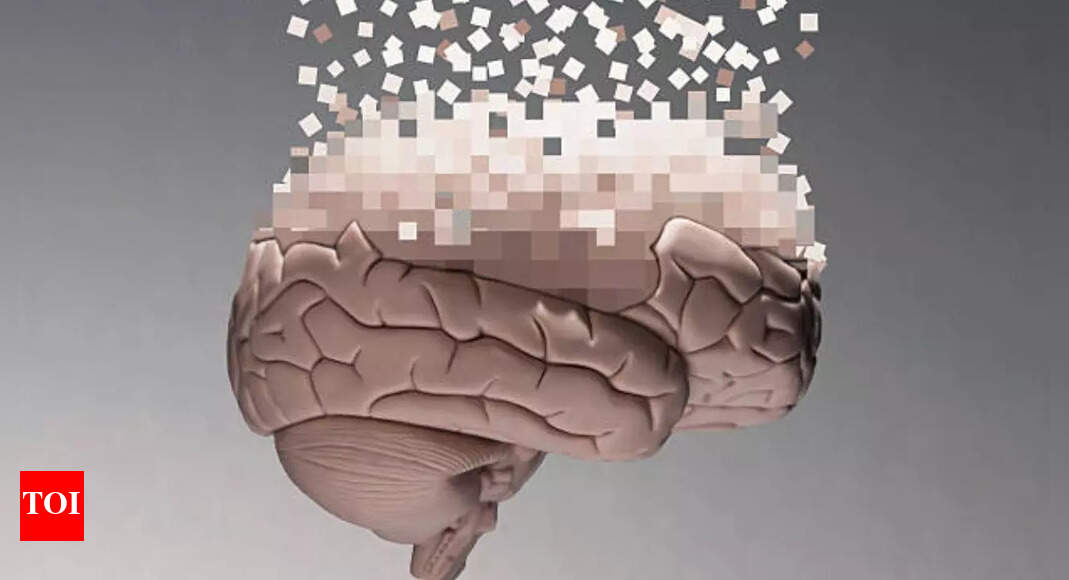
Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is used to treat nerve pain, epilepsy after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting the chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. With every drug having some types of side effects, the ones produced by taking this one include dizziness, drowsiness, headaches and nausea. While these might be more adaptable side effects that can be dealt with easily, a new study has revealed one side effect of the consumption of gabapentin that has more long-term effects than ever known before. Case Western University in Cleveland performed a study to find that gabapentin can significantly increase the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in people consuming it for lower chronic back pain. “Our findings indicate an association between gabapentin prescription and dementia or cognitive impairment within 10 years. Moreover, increased gabapentin prescription frequency correlated with dementia incidence,” wrote the study authors in the study published in the journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.
Does gabapentin really increase the risk of dementia?
In order to carry out the research, the researchers examined the records of over 26,400 patients who had been prescribed gabapentin for persistent low back pain between 2004 and 2024 and 26,400 patients who had not been prescribed the drug.After considering differentiating factors such as patient demographics, medical history and use of other painkillers, the researchers revealed that those who had received 6 or more gabapentin prescriptions were 29% more likely to be diagnosed with dementia. These people were 85% more likely to be diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment within 10 years of back pain diagnosis.While dementia typically affects older adults over the age of 65, due to the consumption of gabapentin, the risk of dementia more than doubled among people between the ages of 35-49. Additionally, the risk of mild cognitive impairment more than tripled. Similar effects were seen in people between 50-64 years old.Here, the frequency of use was a deciding factor as well. Those with 12 or more prescriptions were 40% more likely to develop dementia and 65% more likely to develop mild cognitive impairment as compared to those who had 3-11 prescriptions.Gabapentin was approved by the FDA in 1993 to control partial seizures in epilepsy patients older than 12. It was initially considered to have a low potential for abuse or dependence.However, recently various cases of its side effects have been on the rise. Research published in Pain Medicine highlighted how gabapentin exposure was associated with hospitalisation for all ages, even at low doses.The results of the study associating gabapentin with a higher risk of dementia support the monitoring of adult patients prescribed the drug to monitor their potential cognitive decline.Along with drug consumption, other risks of dementia are traumatic brain injury, untreated hearing loss, depression, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity and smoking. The ideal way to reduce these risks is to stop smoking and alcohol consumption, have a healthy diet and regular exercise.